Cold war map europe 1945 worksheet answers – Delving into the depths of Cold War history, we embark on an exploration of the Cold War Map of Europe 1945 Worksheet Answers, uncovering the intricate political and territorial transformations that reshaped Europe in the aftermath of World War II.
The division of Europe, influenced by the Yalta and Potsdam Conferences, sowed the seeds of ideological conflict, with the Iron Curtain serving as a potent symbol of this divide. Major powers like the United States, Soviet Union, Great Britain, and France played pivotal roles in shaping the Cold War landscape.
European Division after World War II: Cold War Map Europe 1945 Worksheet Answers
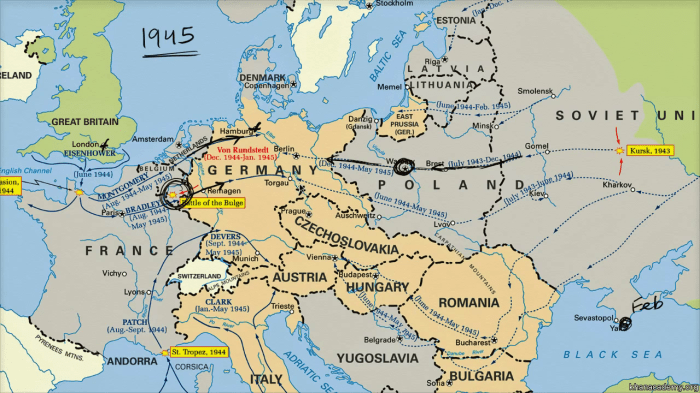
After the conclusion of World War II, Europe underwent significant political and territorial changes. The victorious Allied powers, primarily the United States, the Soviet Union, and Great Britain, played a crucial role in shaping the post-war order. The Yalta Conference in February 1945 and the Potsdam Conference in July-August 1945 were key events that laid the groundwork for the division of Europe.
The Yalta Conference resulted in agreements on the division of Germany into four occupation zones and the establishment of a Council of Foreign Ministers to prepare peace treaties with Germany and its allies. The Potsdam Conference confirmed these decisions and also established the Oder-Neisse Line as the eastern border of Germany and the Soviet Union’s control over Eastern Europe.
Key Features of the Cold War Map of Europe
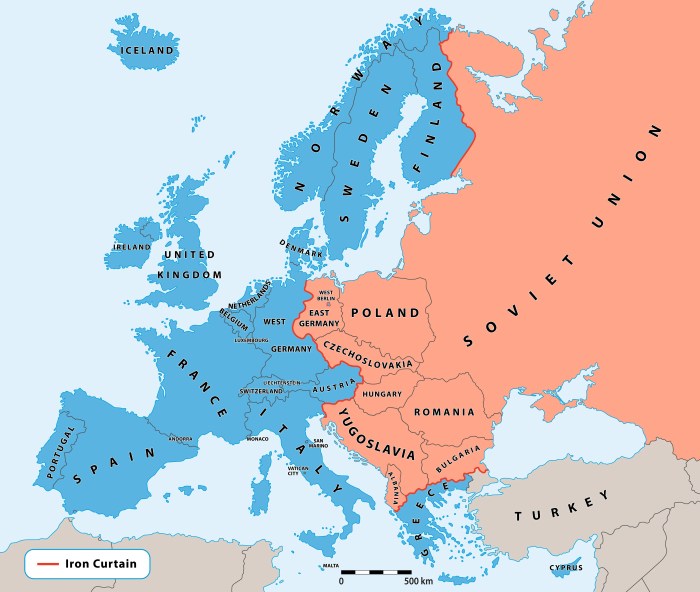
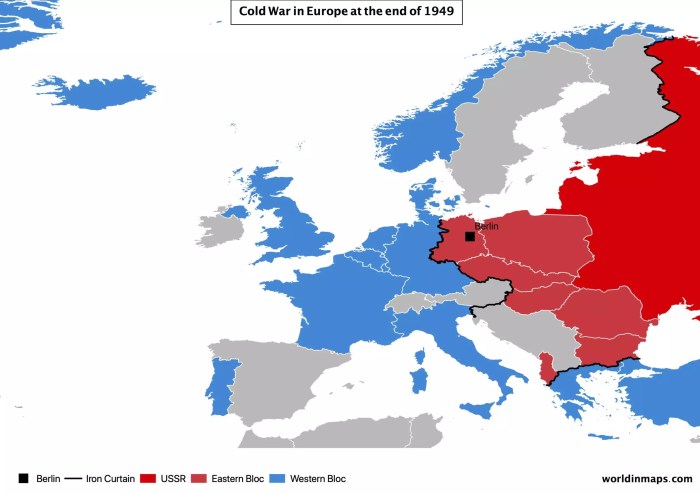
The Cold War, an era of political and ideological tension between the United States and the Soviet Union, had a profound impact on the map of Europe. The continent was divided into two major political and ideological blocs: the Eastern Bloc and the Western Bloc.
The Eastern Bloc consisted of countries under the influence of the Soviet Union, including East Germany, Poland, Czechoslovakia, Hungary, Romania, Bulgaria, and Albania. The Western Bloc consisted of countries aligned with the United States and its allies, including West Germany, France, Great Britain, Italy, and the Benelux countries.
The Iron Curtain, a symbolic and physical barrier, separated the Eastern and Western Blocs. It was a line of fortifications and border controls that prevented movement between the two blocs and symbolized the ideological divide between the Soviet Union and its Western adversaries.
Eastern Bloc Countries
- East Germany
- Poland
- Czechoslovakia
- Hungary
- Romania
- Bulgaria
- Albania
The Eastern Bloc countries were characterized by communist governments, centrally planned economies, and limited political freedoms. The Soviet Union exerted significant control over its satellite states, often through the presence of Soviet troops and the installation of loyalist governments.
For example, in Czechoslovakia, the Communist Party of Czechoslovakia seized power in 1948 and established a totalitarian regime. In Hungary, the Soviet Union intervened militarily in 1956 to suppress a popular uprising against the communist government.
Western Bloc Countries, Cold war map europe 1945 worksheet answers
- West Germany
- France
- Great Britain
- Italy
- Benelux countries (Belgium, Netherlands, Luxembourg)
The Western Bloc countries were characterized by democratic governments, market economies, and strong ties to the United States. The United States provided significant economic and military aid to Western Europe through the Marshall Plan and the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO).
For example, the United States provided military assistance to Greece and Turkey to prevent their falling under Soviet influence. The United States also played a key role in the Berlin Airlift, which supplied West Berlin with food and supplies after the Soviet Union blockaded the city in 1948.
Flashpoints of the Cold War
- Berlin Blockade (1948-1949)
- Cuban Missile Crisis (1962)
- Berlin Wall (1961-1989)
The Cold War was marked by several major crises that brought the world to the brink of nuclear war. These flashpoints included the Berlin Blockade, the Cuban Missile Crisis, and the Berlin Wall.
During the Berlin Blockade, the Soviet Union blockaded West Berlin in an attempt to force the Western powers to withdraw from the city. The United States responded with the Berlin Airlift, which successfully supplied West Berlin with food and supplies.
FAQ Corner
What were the key features of the Cold War Map of Europe?
The Cold War Map of Europe was characterized by the emergence of major political and ideological blocs, physical and symbolic barriers like the Iron Curtain, and the influence of key countries like the United States, Soviet Union, Great Britain, and France.
What were the major areas of conflict and tension in Europe during the Cold War?
Major flashpoints of the Cold War in Europe included the Berlin Blockade, the Cuban Missile Crisis, and the Berlin Wall, each representing moments of heightened tension and strategic maneuvering by both sides.