The ubiquitous plastic wrap, a staple in kitchens and households worldwide, has sparked scientific inquiry into its fundamental nature. Is plastic wrap homogeneous or heterogeneous? Delving into the composition, physical properties, and microscopic structure of this versatile material, this exploration unravels the intricacies that define its unique characteristics.
Composed primarily of polyethylene, plastic wrap exhibits a remarkable molecular structure that contributes to its exceptional properties. Its transparency, flexibility, and water resistance make it an ideal choice for food storage, packaging, and various industrial applications. However, beneath its seemingly uniform appearance lies a complex microscopic landscape that reveals the true nature of plastic wrap.
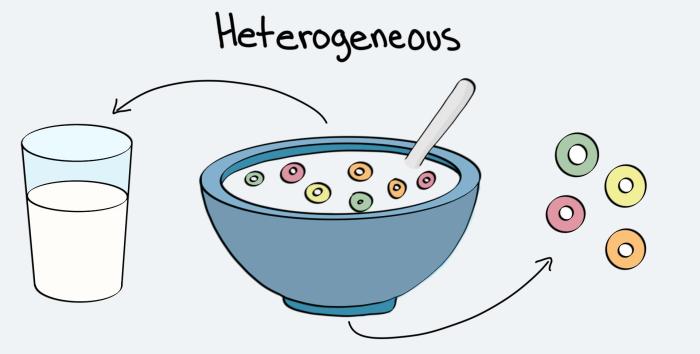
1. Homogeneity vs. Heterogeneity

Homogeneityrefers to the uniform composition and properties throughout a substance. Heterogeneity, on the other hand, describes a substance with varying composition and properties.
Examples of homogeneous materials:pure water, salt, gold
Examples of heterogeneous materials:granite, soil, wood
2. Composition of Plastic Wrap

Plastic wrap is primarily composed of polyethylene, a synthetic polymer made from ethylene monomers. Its chemical formula is (C2H4)n.
The molecular structure of polyethylene consists of long, repeating chains of carbon atoms with hydrogen atoms attached. This structure gives plastic wrap its flexibility and strength.
3. Physical Properties of Plastic Wrap
Transparency
Plastic wrap is highly transparent, allowing light to pass through it easily. This property makes it ideal for food packaging, as it allows consumers to see the contents.
Flexibility, Is plastic wrap homogeneous or heterogeneous
The molecular structure of plastic wrap gives it exceptional flexibility. It can be easily stretched and conformed to various shapes, making it suitable for wrapping irregular objects.
Water Resistance
Plastic wrap is waterproof, preventing moisture from passing through. This property makes it an effective barrier against spoilage and contamination in food storage.
4. Microscopic Structure of Plastic Wrap
Under a microscope, plastic wrap appears as a network of long, intertwined polymer chains. These chains are arranged in a semi-crystalline structure, with crystalline regions interspersed with amorphous regions.
The crystalline regions are more densely packed and provide strength and rigidity, while the amorphous regions are less ordered and contribute to flexibility.
5. Chemical Reactivity of Plastic Wrap
Plastic wrap is generally chemically inert, meaning it does not react readily with most substances. However, it can be degraded by strong acids and bases.
It is also susceptible to oxidation, which can occur over time or when exposed to high temperatures. Oxidation can lead to the formation of free radicals, which can weaken the polymer chains and reduce the wrap’s strength.
6. Applications of Plastic Wrap
Food Storage
Plastic wrap is widely used in food storage to preserve freshness, prevent contamination, and extend shelf life.
Packaging
In the packaging industry, plastic wrap is used to protect products from moisture, dust, and damage during transportation and storage.
Other Applications
Plastic wrap also has various other applications, such as:
- Preventing paint spills during painting
- Covering plants to protect them from frost
- Creating temporary greenhouses
- Wrapping medical instruments for sterilization
7. Environmental Considerations
Plastic wrap is not biodegradable and can accumulate in the environment, posing a threat to wildlife and ecosystems.
However, there are ongoing efforts to develop biodegradable alternatives to plastic wrap, such as those made from plant-based materials.
8. Alternatives to Plastic Wrap: Is Plastic Wrap Homogeneous Or Heterogeneous
Several alternatives to plastic wrap are available, including:
Reusable Containers
Reusable containers, such as glass jars and silicone bags, are a sustainable option for food storage.
Beeswax Wraps
Beeswax wraps are made from cotton or hemp coated with beeswax and other natural resins. They are biodegradable and can be reused multiple times.
Biodegradable Films
Biodegradable films made from plant-based materials, such as cellulose or starch, are an environmentally friendly alternative to plastic wrap.
FAQ Explained
Is plastic wrap completely homogeneous?
While plastic wrap appears uniform, microscopic examination reveals a heterogeneous structure with variations in molecular arrangement and density.
What factors contribute to the heterogeneity of plastic wrap?
Variations in molecular weight, crystallinity, and orientation during the manufacturing process can lead to heterogeneous regions within the material.
How does the heterogeneity of plastic wrap affect its properties?
Heterogeneity can influence the mechanical strength, barrier properties, and optical clarity of plastic wrap, affecting its performance in specific applications.