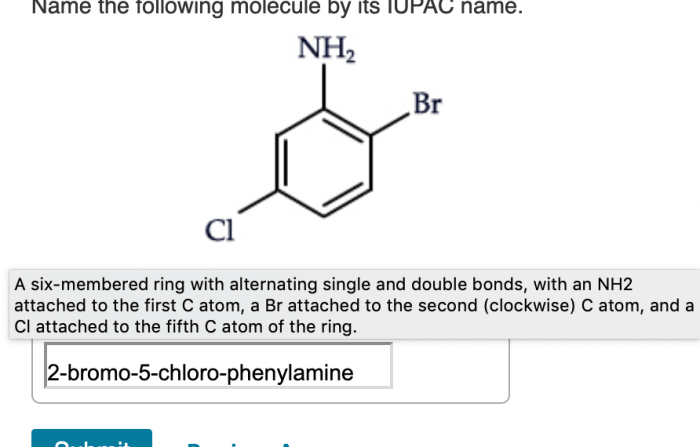
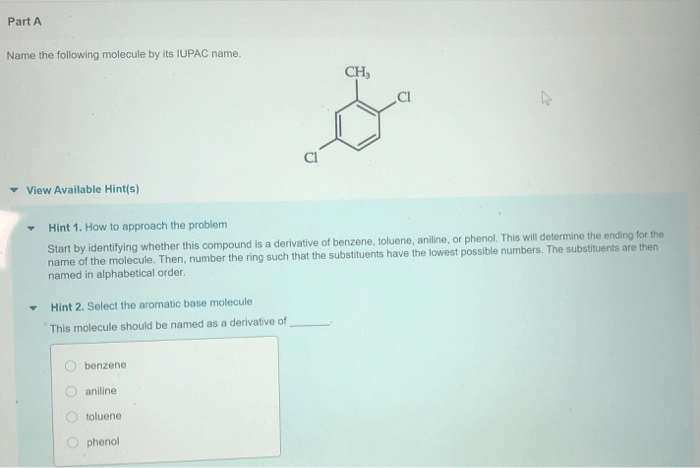
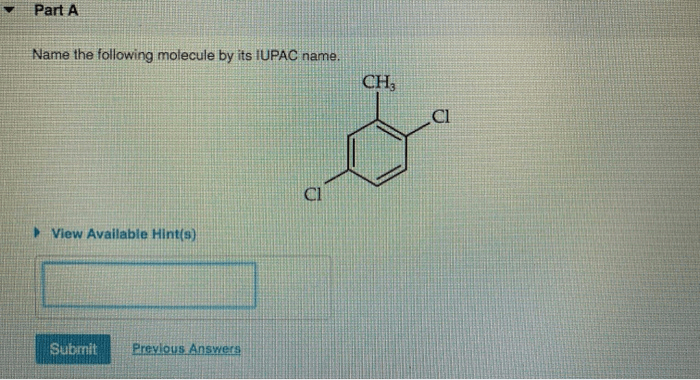
Name the following molecule by its iupac name – Delve into the realm of IUPAC nomenclature, where the intricacies of naming organic compounds unravel before your eyes. This comprehensive guide empowers you with the knowledge to decipher the language of chemistry, unlocking the secrets of molecular identities.
Unveiling the principles established by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC), we embark on a journey to unravel the systematic approach to naming organic molecules. Prepare to navigate the diverse landscape of functional groups, isomers, and the nuances that distinguish common names from IUPAC nomenclature.
1. IUPAC Nomenclature
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) has established a set of rules for naming organic compounds. These rules provide a systematic and unambiguous way to identify and describe organic molecules.
The IUPAC nomenclature system is based on the following principles:
- The name of an organic compound is derived from its structure.
- The name of a parent chain is based on the number of carbon atoms in the chain.
- The names of functional groups are added to the name of the parent chain.
- The names of substituents are added to the name of the parent chain.
For example, the IUPAC name for the following compound is 2-propanol:
The parent chain is propane, which has three carbon atoms. The functional group is the hydroxyl group (-OH). The substituent is the methyl group (-CH 3). The name of the compound is derived from the parent chain (propane), the functional group (ol), and the substituent (2-).
2. Identifying Functional Groups
Functional groups are groups of atoms that have characteristic chemical properties. The presence of a functional group in an organic molecule determines the molecule’s chemical reactivity and physical properties.
The most common functional groups are:
- Alkanes: contain only carbon and hydrogen atoms, and have the general formula C nH 2n+2
- Alkenes: contain at least one carbon-carbon double bond, and have the general formula C nH 2n
- Alkynes: contain at least one carbon-carbon triple bond, and have the general formula C nH 2n-2
- Alcohols: contain a hydroxyl group (-OH), and have the general formula R-OH
- Aldehydes: contain a carbonyl group (-C=O), and have the general formula R-CHO
- Ketones: contain a carbonyl group (-C=O), and have the general formula R 2C=O
- Carboxylic acids: contain a carboxyl group (-COOH), and have the general formula R-COOH
- Esters: contain an ester group (-COOR), and have the general formula R-COOR’
- Amides: contain an amide group (-CONH 2), and have the general formula R-CONH 2
- Amines: contain an amino group (-NH 2), and have the general formula R-NH 2
3. Naming Molecules by IUPAC Name
To name an organic molecule using IUPAC nomenclature, follow these steps:
- Identify the parent chain. The parent chain is the longest chain of carbon atoms in the molecule.
- Identify the functional group. The functional group is the group of atoms that determines the molecule’s chemical reactivity and physical properties.
- Number the carbon atoms in the parent chain. The carbon atom that is attached to the functional group is assigned the number 1.
- Name the substituents. The substituents are the atoms or groups of atoms that are attached to the parent chain.
- Combine the name of the parent chain, the name of the functional group, and the names of the substituents to form the IUPAC name of the molecule.
For example, the IUPAC name for the following compound is 2-propanol:
The parent chain is propane, which has three carbon atoms. The functional group is the hydroxyl group (-OH). The substituent is the methyl group (-CH 3). The name of the compound is derived from the parent chain (propane), the functional group (ol), and the substituent (2-).
4. Common Name vs. IUPAC Name
Common names are often used for organic compounds, but IUPAC names are more systematic and unambiguous. IUPAC names are preferred in scientific writing and when discussing organic compounds with other chemists.
The following table compares common names and IUPAC names for some common organic compounds:
| Common Name | IUPAC Name |
|---|---|
| Methane | Methane |
| Ethane | Ethane |
| Propane | Propane |
| Butane | Butane |
| Pentane | Pentane |
| Hexane | Hexane |
| Benzene | Benzene |
| Toluene | Methylbenzene |
| Xylene | Dimethylbenzene |
| Ethanol | Ethanol |
| Propanol | Propanol |
| Butanol | Butanol |
| Pentanol | Pentanol |
| Hexanol | Hexanol |
| Formaldehyde | Methanal |
| Acetaldehyde | Ethanal |
| Acetone | Propanone |
| Acetic acid | Ethanoic acid |
| Propionic acid | Propanoic acid |
| Butyric acid | Butanoic acid |
| Valeric acid | Pentanoic acid |
| Caproic acid | Hexanoic acid |
5. Isomers and IUPAC Naming: Name The Following Molecule By Its Iupac Name
Isomers are molecules that have the same molecular formula but different structures. Isomers can have different physical and chemical properties.
There are two main types of isomers: structural isomers and stereoisomers.
- Structural isomers have the same molecular formula but different arrangements of atoms.
- Stereoisomers have the same molecular formula and the same arrangement of atoms but different orientations of atoms in space.
For example, the following two compounds are structural isomers of each other:
The first compound is a straight-chain hydrocarbon, while the second compound is a branched-chain hydrocarbon.
The following two compounds are stereoisomers of each other:
The first compound is a cis isomer, while the second compound is a trans isomer.
When naming isomers, it is important to use the correct IUPAC nomenclature. The IUPAC nomenclature system provides a way to unambiguously identify and describe isomers.
Essential Questionnaire
What is the significance of IUPAC nomenclature?
IUPAC nomenclature provides a standardized and unambiguous system for naming organic compounds, facilitating clear communication and accurate identification among scientists worldwide.
How do functional groups influence the properties of organic compounds?
Functional groups impart characteristic chemical and physical properties to organic compounds, influencing their reactivity, solubility, and biological activity.
What are the key differences between common names and IUPAC names?
Common names are often based on historical or trivial origins, while IUPAC names are systematic and derived from the structural features of the molecule, ensuring consistency and precision.