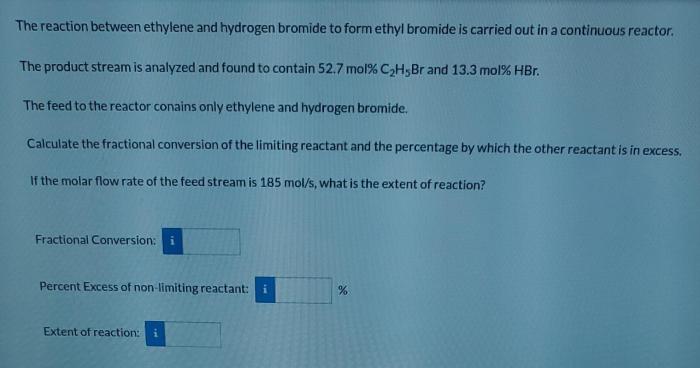
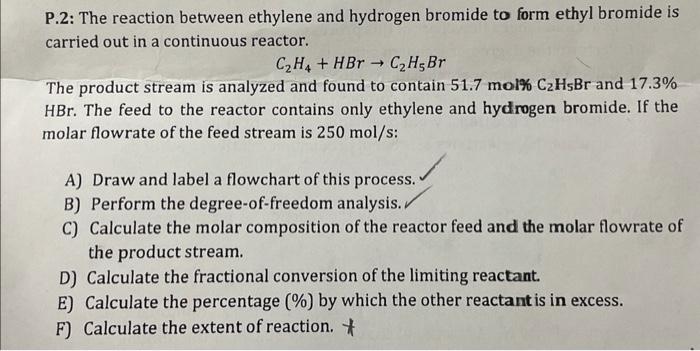
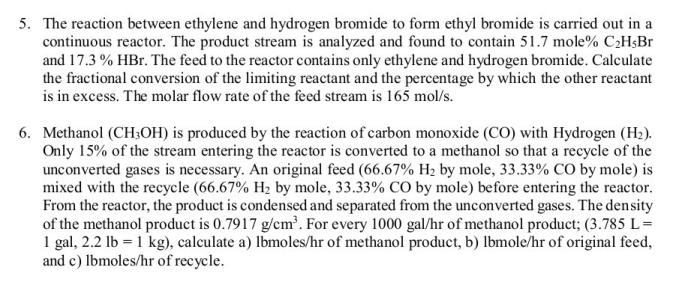
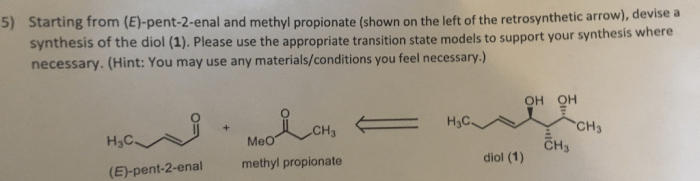
The reaction between ethylene and hydrogen bromide, a cornerstone in the realm of chemistry, holds immense significance in both academic and industrial domains. This reaction, characterized by its unique mechanism and diverse applications, offers a captivating journey into the intricacies of organic chemistry.
This intricate reaction involves the addition of hydrogen bromide to the double bond of ethylene, leading to the formation of various products depending on the reaction conditions. It finds widespread application in the production of important chemicals, including ethyl bromide, a versatile intermediate in organic synthesis.
The Reaction between Ethylene and Hydrogen Bromide

The reaction between ethylene and hydrogen bromide is an important industrial process that is used to produce a variety of chemicals and materials. This reaction is also of interest to chemists because it is a simple and well-studied example of an electrophilic addition reaction.
In this reaction, ethylene (C2H4) reacts with hydrogen bromide (HBr) to form ethyl bromide (C2H5Br). The reaction is catalyzed by a strong acid, such as sulfuric acid (H2SO4). The mechanism of the reaction is as follows:
Mechanism of the Reaction
The first step of the reaction is the protonation of ethylene by the acid catalyst. This forms a carbocation intermediate, which is a positively charged carbon atom. The carbocation is then attacked by the bromide ion (Br-) to form ethyl bromide.
The rate of the reaction is affected by a number of factors, including the temperature, pressure, and concentration of the reactants. The equilibrium constant for the reaction is also important, as it determines the relative amounts of reactants and products that are present at equilibrium.
Stereochemistry of the Reaction, The reaction between ethylene and hydrogen bromide
The reaction between ethylene and hydrogen bromide is a stereospecific reaction, meaning that the stereochemistry of the reactants determines the stereochemistry of the product. In this case, the reaction produces a mixture of cis and trans isomers of ethyl bromide.
The cis isomer is formed when the hydrogen and bromine atoms are on the same side of the double bond. The trans isomer is formed when the hydrogen and bromine atoms are on opposite sides of the double bond.
Applications of the Reaction
The reaction between ethylene and hydrogen bromide is used to produce a variety of chemicals and materials, including:
- Ethyl bromide, which is used as a solvent and as a starting material for the synthesis of other chemicals.
- Polyethylene, which is a common plastic.
- Polyvinyl chloride (PVC), which is used to make a variety of products, including pipes, flooring, and siding.
Safety Considerations
The reaction between ethylene and hydrogen bromide is a hazardous reaction that can produce toxic fumes. It is important to take proper safety precautions when handling these chemicals.
Some of the safety precautions that should be taken include:
- Working in a well-ventilated area.
- Wearing gloves and eye protection.
- Using a fume hood.
Question & Answer Hub
What is the significance of the reaction between ethylene and hydrogen bromide?
This reaction holds great importance due to its role in the production of ethyl bromide, a crucial intermediate in organic synthesis.
How does the reaction mechanism influence the outcome of the reaction?
The reaction mechanism, involving the formation of a carbocation intermediate, plays a critical role in determining the regioselectivity and stereochemistry of the products formed.
What factors affect the rate and yield of the reaction?
Factors such as temperature, pressure, and concentration significantly influence the rate and yield of the reaction, with higher temperatures and concentrations generally favoring the formation of the desired products.