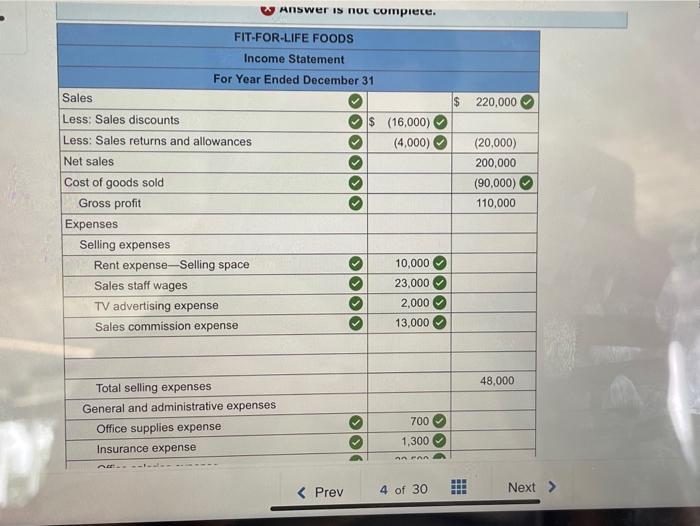
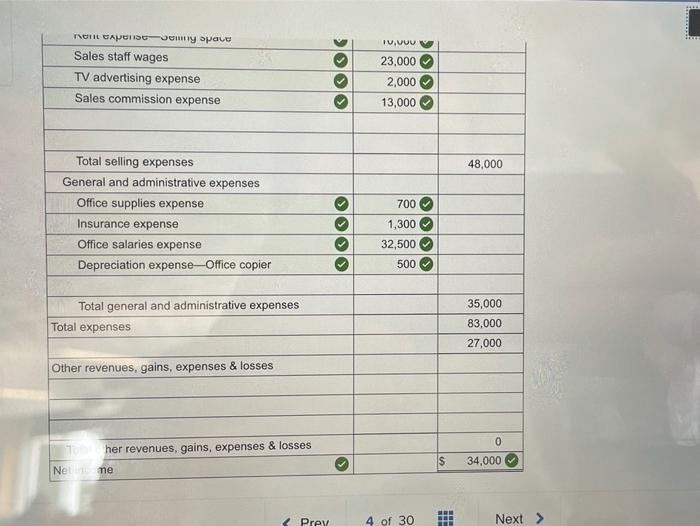
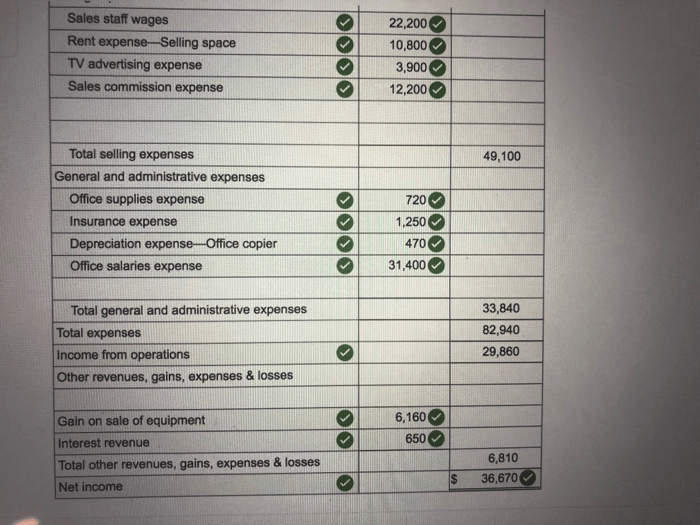
Fit for Life Foods reports the following income statement, providing valuable insights into the company’s financial performance and overall health. This comprehensive analysis will delve into key components, trends, and industry comparisons, offering a thorough understanding of the company’s financial standing and future prospects.
The income statement is a crucial financial document that summarizes a company’s revenues, expenses, and profits over a specific period. It serves as a fundamental tool for evaluating a company’s financial performance, profitability, and overall health.
Income Statement Overview
An income statement, also known as a profit and loss statement, is a financial document that summarizes a company’s financial performance over a specific period, typically a quarter or a year. It provides insights into the company’s revenue, expenses, and profits.
The income statement is a crucial tool for financial analysis, as it helps investors, creditors, and management assess the company’s financial health, profitability, and overall performance. It allows them to evaluate the company’s ability to generate revenue, control costs, and ultimately generate profits.
Key Components of an Income Statement, Fit for life foods reports the following income statement
- Revenue: This represents the income generated by the company from its primary operations, such as sales of goods or services.
- Expenses: These are the costs incurred by the company in generating revenue, including operating expenses, interest expenses, and taxes.
- Gross Profit: This is the difference between revenue and the cost of goods sold, which represents the profit earned from the company’s core operations.
- Operating Profit: This is the gross profit minus operating expenses, which represents the profit earned from the company’s operating activities.
- Net Income: This is the bottom line of the income statement and represents the profit earned by the company after deducting all expenses, including non-operating expenses and taxes.
Revenue
Revenue is the income generated by a company from its primary operations, such as the sale of goods or services. It is recognized when the company earns the right to receive payment for the goods or services provided.
Fit for Life Foods generates revenue primarily through the sale of its healthy food products, including meal kits, snacks, and beverages. The company also generates revenue from its fitness programs and online subscription services.
Revenue is typically measured at the point of sale, when the customer makes the purchase. The amount of revenue recognized is equal to the fair value of the goods or services provided.
Expenses: Fit For Life Foods Reports The Following Income Statement
Expenses are the costs incurred by a company in generating revenue. They are classified into two main categories: operating expenses and non-operating expenses.
Operating expenses are the costs directly related to the company’s core operations, such as:
- Cost of goods sold: This includes the direct costs of producing the goods sold, such as raw materials, labor, and manufacturing overhead.
- Selling, general, and administrative expenses (SG&A): These are the costs associated with selling and marketing the company’s products, as well as general administrative expenses, such as salaries, rent, and utilities.
Non-operating expenses are the costs that are not directly related to the company’s core operations, such as interest expenses, foreign exchange losses, and gains on the sale of assets.
Gross Profit
Gross profit is the difference between revenue and the cost of goods sold. It represents the profit earned from the company’s core operations.
Gross profit is an important measure of profitability, as it indicates the company’s ability to generate profit from its sales. A higher gross profit margin, which is calculated as gross profit divided by revenue, indicates that the company is able to generate more profit from each dollar of sales.
Factors that can influence gross profit margin include the cost of goods sold, product mix, and pricing strategies.
Operating Profit
Operating profit is the gross profit minus operating expenses. It represents the profit earned from the company’s operating activities.
Operating profit is a key measure of a company’s profitability, as it excludes non-operating expenses, which can be volatile and unrelated to the company’s core operations.
Factors that can affect operating profit margin, which is calculated as operating profit divided by revenue, include the efficiency of the company’s operations, its ability to control costs, and its pricing strategies.
Net Income
Net income is the bottom line of the income statement and represents the profit earned by the company after deducting all expenses, including non-operating expenses and taxes.
Net income is the most comprehensive measure of a company’s profitability, as it takes into account all sources of revenue and expenses.
Factors that can influence net income margin, which is calculated as net income divided by revenue, include the company’s overall profitability, its tax burden, and its capital structure.
Financial Ratios
Financial ratios are metrics that are calculated using data from the income statement. They provide insights into a company’s financial health and performance.
Key financial ratios that can be derived from the income statement include:
- Gross profit margin: This ratio measures the percentage of revenue that is generated as gross profit.
- Operating profit margin: This ratio measures the percentage of revenue that is generated as operating profit.
- Net income margin: This ratio measures the percentage of revenue that is generated as net income.
- Return on assets (ROA): This ratio measures the percentage of return that the company generates on its total assets.
- Return on equity (ROE): This ratio measures the percentage of return that the company generates on its shareholders’ equity.
Industry Comparison
Comparing a company’s income statement to industry benchmarks can provide insights into the company’s performance relative to its peers.
Fit for Life Foods can compare its income statement to industry benchmarks to identify areas where the company is performing well or lagging behind.
This comparison can help the company identify opportunities for improvement and make informed decisions about its operations and strategies.
Trend Analysis
Analyzing trends in a company’s income statement over time can provide insights into the company’s financial performance and identify potential areas of concern.
Fit for Life Foods can analyze trends in its income statement to identify any significant changes or patterns.
This analysis can help the company understand the drivers of its financial performance and make informed decisions about its future strategies.
Limitations and Considerations
While the income statement is a valuable tool for financial analysis, it is important to be aware of its limitations.
- The income statement is based on historical data and may not reflect future performance.
- The income statement can be affected by accounting policies and estimates, which can vary from company to company.
- The income statement does not provide a complete picture of a company’s financial health and should be used in conjunction with other financial statements.
Expert Answers
What is the purpose of an income statement?
An income statement provides a snapshot of a company’s financial performance over a specific period, summarizing its revenues, expenses, and profits.
What are the key components of an income statement?
Key components of an income statement include revenue, expenses, gross profit, operating profit, and net income.
How can financial ratios be used to analyze an income statement?
Financial ratios derived from an income statement, such as gross profit margin and net profit margin, can provide valuable insights into a company’s profitability and efficiency.