Which of the following statements is true of research samples? This question lies at the heart of understanding the fundamental principles of research methodology. Research samples play a pivotal role in scientific investigations, providing researchers with a window into the characteristics of a larger population.
In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of research samples, exploring their significance, types, characteristics, selection methods, ethical considerations, and reporting guidelines. Join us on this enlightening journey as we unravel the complexities of research sampling, empowering you with the knowledge to conduct rigorous and reliable research studies.
Research samples are subsets of a larger population that are selected to represent the entire group. They provide researchers with valuable insights into the characteristics and behaviors of the population, enabling them to make inferences about the larger group based on the data collected from the sample.
Understanding Research Samples
Research samples are a subset of a population that researchers study to make inferences about the entire population. They play a crucial role in research as they provide insights into the characteristics, behaviors, and opinions of a larger group. Understanding research samples is essential for evaluating the validity and reliability of research findings.
There are two main types of research samples: probability samples and non-probability samples. Probability samples are selected randomly, ensuring that every member of the population has an equal chance of being included. This type of sampling allows researchers to make generalizations about the population based on the sample.
Non-probability samples are selected based on convenience or specific criteria. They are not random and may not accurately represent the population. However, non-probability samples can be useful for exploratory research or when it is not feasible to obtain a probability sample.
Characteristics of Research Samples
Key characteristics of research samples include representativeness, size, and accessibility. Representativeness refers to how well the sample reflects the characteristics of the population. Size refers to the number of participants in the sample. Accessibility refers to how easy it is for researchers to reach and recruit participants.
These characteristics impact the validity and reliability of research findings. A representative sample ensures that the results can be generalized to the population. A large sample size increases the precision of the results. Accessibility can affect the representativeness of the sample if certain groups are more difficult to reach.
Selecting Research Samples
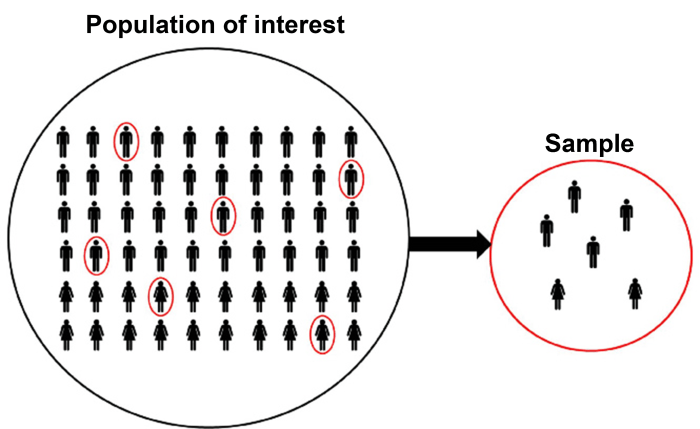
Selecting an appropriate research sample is crucial for obtaining meaningful results. Researchers must consider the purpose of the research, the characteristics of the population, and the resources available. There are various sampling methods, each with its advantages and disadvantages.
Probability sampling methods include simple random sampling, systematic sampling, stratified sampling, and cluster sampling. Non-probability sampling methods include convenience sampling, purposive sampling, and snowball sampling.
Ethical Considerations in Research Sampling
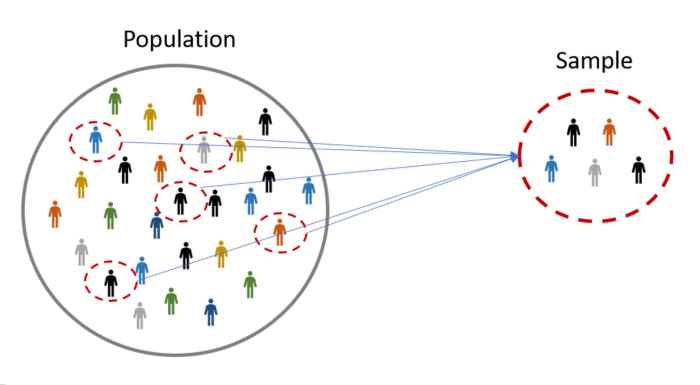
Ethical considerations are paramount in research sampling. Researchers must obtain informed consent from participants, ensuring they understand the purpose of the research and their rights. Privacy and confidentiality must be maintained to protect participants’ personal information.
Researchers should avoid sampling bias, which occurs when the sample is not representative of the population. This can lead to inaccurate results and incorrect conclusions. Ethical guidelines and institutional review boards help ensure that research samples are selected in an ethical and responsible manner.
Advanced Topics in Research Sampling
Advanced sampling techniques, such as stratified sampling, cluster sampling, and multistage sampling, are used in complex research designs. Stratified sampling divides the population into subgroups (strata) and randomly selects participants from each stratum. Cluster sampling selects groups (clusters) of participants, rather than individual participants.
Multistage sampling involves selecting participants in stages, starting with a large group and progressively selecting smaller subgroups. These techniques enhance the representativeness and precision of research samples, but they require more resources and planning.
Reporting Research Samples
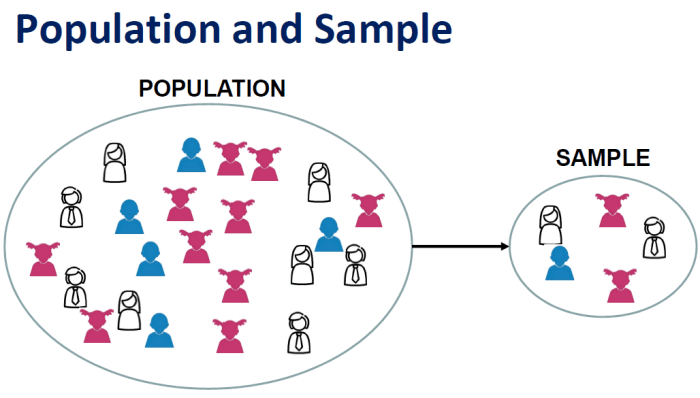
Reporting research samples in publications is essential for transparency and replicability. Researchers should provide detailed information about the sampling method, sample size, and characteristics of the participants. This allows readers to evaluate the validity and reliability of the findings.
Transparency in reporting research samples enables other researchers to replicate the study or conduct further research on the same population. It also allows for cross-study comparisons and the identification of sampling biases or limitations.
FAQ Insights: Which Of The Following Statements Is True Of Research Samples
What is the purpose of a research sample?
The purpose of a research sample is to provide researchers with a representative subset of a larger population, allowing them to make inferences about the entire group based on the data collected from the sample.
What are the different types of research samples?
There are two main types of research samples: probability samples and non-probability samples. Probability samples are selected randomly, giving each member of the population an equal chance of being included in the sample. Non-probability samples are selected based on convenience or other non-random criteria.
What are the key characteristics of a good research sample?
A good research sample should be representative of the larger population, of sufficient size to provide meaningful data, and accessible to the researcher.